shelf 1
Earthenware, the first clay body humans fired, can be left unglazed for dry goods, although glaze is required for wares containing liquids and serving foods. Harder and more durable than earthenware, stoneware vessels can hold liquid even when unglazed, but they become more resistant when glaze is added. Stoneware was often the preferred clay body for storage vessels—especially for commodities shipped across the seas or transported on overland journeys.
Click an object to learn more
Images

Persian (Iran, Seljuk Empire 1037–1194)
Ewer, 1200s
Earthenware with glaze
Museum Appropriation Fund 27.114

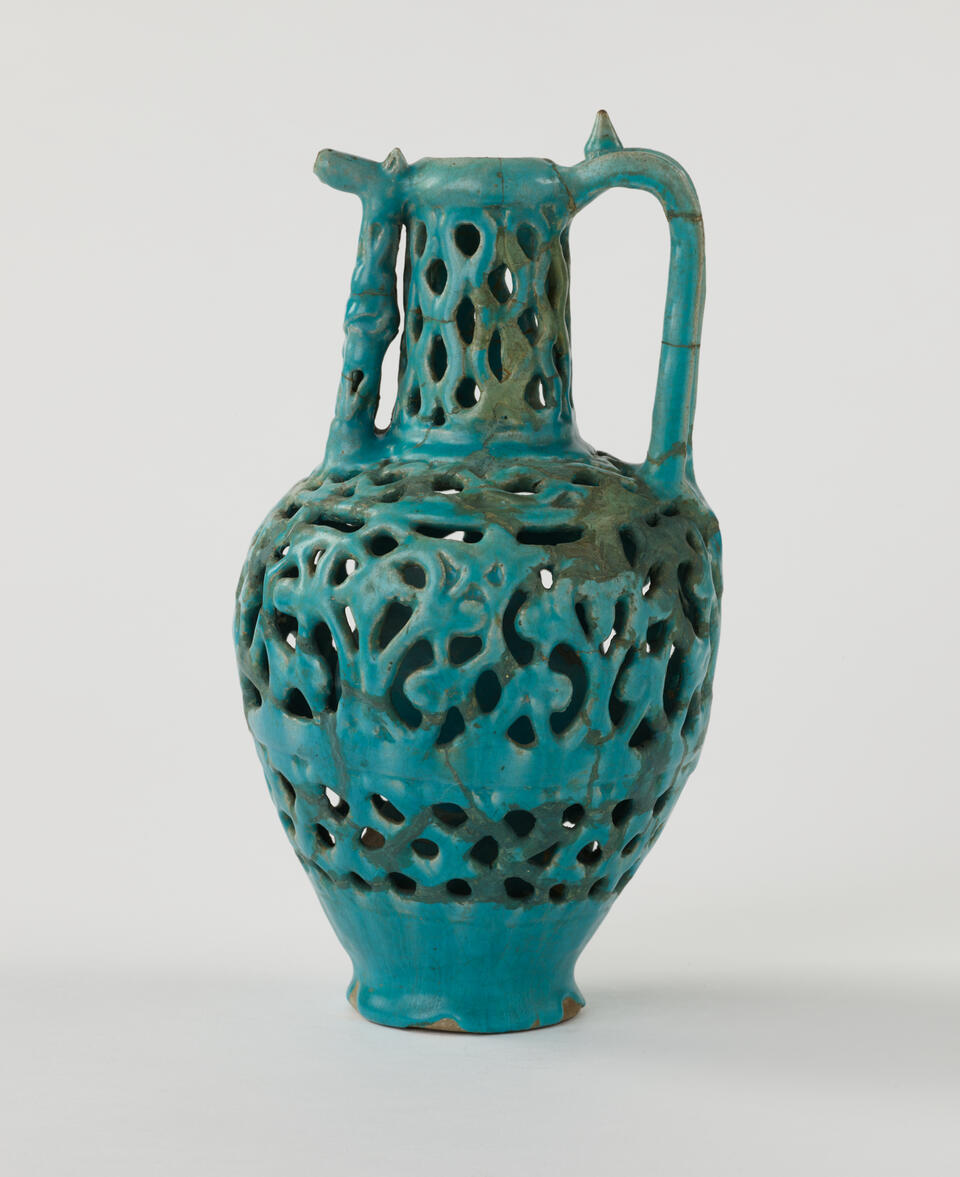
German
Pitcher, ca. 1575
Earthenware with lead glaze
Anonymous gift 49.069

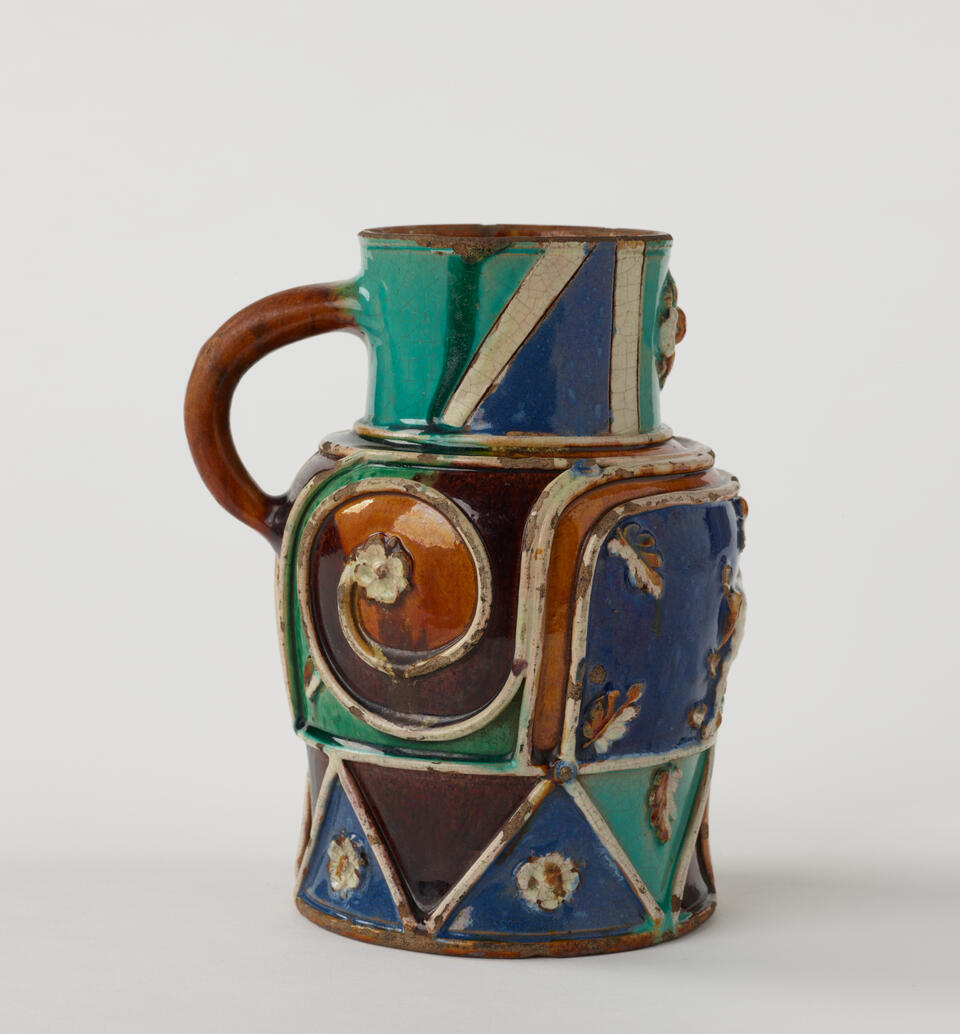
American
Jug, early 1800s
Stoneware with glaze
Gift of the Estate of Mrs. Gustav Radeke 31.523